Arrange Your Dermal Filler Session with Dr. Laura Geige
Understanding the Mechanisms
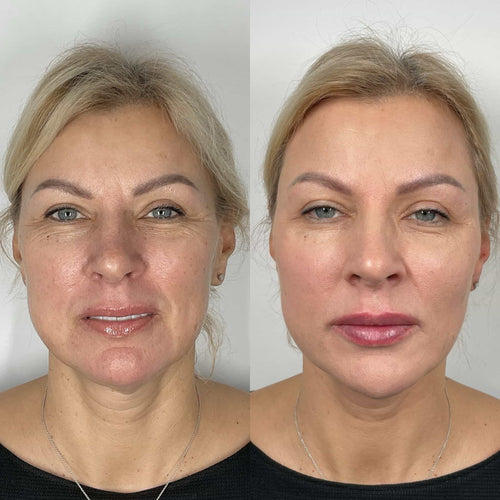
Botulinum Toxin
Botulinum toxin, commonly known as Botox, is a neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium *Clostridium botulinum*. It’s renowned for its potent ability to temporarily paralyze muscles by blocking the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter crucial for muscle contraction.
Understanding its mechanism is key to appreciating why it’s used in cosmetic and medical applications.
Here’s a breakdown:
- Binding**: Botulinum toxin molecules bind to specific receptors on the surface of nerve cells called motor neurons. These neurons transmit signals from the brain to muscles, instructing them to contract.
- Internalization**: Upon binding, the toxin is internalized into the neuron through a process called endocytosis.
- Cleavage**: Inside the neuron, botulinum toxin travels to synaptic vesicles, tiny sacs containing acetylcholine. The toxin then acts as a protease, an enzyme that cuts proteins. It specifically cleaves proteins crucial for the fusion of synaptic vesicles with the nerve cell membrane.
- Acetylcholine Blockage**: This cleavage disrupts the process by which acetylcholine is released into the neuromuscular junction, the gap between nerve and muscle. Without acetylcholine, the muscle cannot receive the signal to contract.
The result of this paralysis is temporary muscle relaxation and smoothing. The effects typically last 3-6 months, after which the nerve cells regenerate new proteins, restoring normal function.
While Botox remains a gold standard, there are other neurotoxins that share similar mechanisms and therapeutic applications:
- Dysport: Similar to Botox, Dysport uses botulinum toxin type A but with a slightly different protein structure. This can lead to variations in onset and duration of effects.
- Xeomin**: Another type A botulinum toxin product, Xeomin is notable for lacking certain accessory proteins found in Botox and Dysport. This may make it less prone to developing antibodies against the toxin.
- Jeuveau: This newer product also utilizes type A botulinum toxin but claims to be more refined and provide longer-lasting results.
It’s important to note that while these neurotoxins share fundamental mechanisms, they may have subtle differences in their formulations and efficacy. Consulting with a qualified medical professional is crucial for determining the most suitable treatment option based on individual needs and considerations.
Muscle Relaxation Effects
Understanding muscle relaxation mechanisms is key to appreciating how botulinum toxin, commonly known as Botox, works and identifying potential alternatives.
Botox exerts its muscle-relaxing effect by targeting *acetylcholine*, a neurotransmitter responsible for transmitting signals from nerves to muscles. At the neuromuscular junction, acetylcholine binds to receptors on muscle cells, triggering a cascade of events that ultimately leads to muscle contraction.
Botox works by blocking the release of acetylcholine. The toxin specifically targets and binds to *SNAP-25*, a protein involved in the fusion of synaptic vesicles containing acetylcholine with the presynaptic membrane. This binding prevents acetylcholine from being released into the neuromuscular junction, effectively paralyzing the muscle.
The duration of muscle paralysis depends on the dose administered and the individual’s metabolism. Botox typically lasts for 3-6 months before the body naturally breaks down the toxin.
While there isn’t a serum *directly* comparable to Botox, some alternative treatments aim to achieve similar muscle relaxation effects through different mechanisms:
-
Dysport and **Xeomin** are both botulinum toxins with similar mechanisms of action to Botox. They differ slightly in their formulations and the protein target (though they still affect SNAP-25), potentially leading to variations in efficacy and duration.
-
Muscle relaxants such as cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) and methocarbamol (Robaxin) work by affecting the central nervous system, reducing muscle spasms and pain. They don’t directly target acetylcholine like Botox but can be useful in managing muscle tension.
-
Topical creams and gels containing ingredients like lidocaine or menthol can provide temporary relief from muscle pain and stiffness by desensitizing nerve endings. These treatments do not affect the underlying mechanism of muscle contraction.
It’s important to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment for individual needs.
Potential Alternatives
Injectable Neuromodulators
While Botox remains the most well-known and widely used injectable neuromodulator, several alternatives exist that achieve similar results by temporarily relaxing facial muscles.
One primary alternative is Dysport. It contains a different formulation of botulinum toxin type A, which may spread more easily under the skin, potentially requiring fewer injections to achieve the desired effect.
Xeomin is another option that utilizes purified botulinum toxin type A with no added proteins. This unique composition aims to minimize the risk of developing antibodies to the toxin over time.
Jeuveau, a relatively newer entrant, also employs botulinum toxin type A and has been shown in clinical trials to effectively reduce moderate to severe frown lines.
It’s essential to remember that individual results may vary depending on factors such as the specific muscle being targeted, injection technique, and patient anatomy. Consultation with a qualified medical professional specializing in injectables is crucial for determining the most suitable option based on individual needs and goals.
Topical Solutions
While no serum can perfectly replicate the effects of Botox, there are several options that offer similar benefits by targeting muscle contractions and fine lines.
Peptides are a popular ingredient in many anti-aging serums. Certain peptides, like Argireline and SNAP-8, work by mimicking the effects of Botox, temporarily relaxing facial muscles and reducing the appearance of wrinkles.
Hyaluronic acid is another powerful humectant that draws moisture into the skin, plumping it up and minimizing the appearance of fine lines. Serums with high concentrations of hyaluronic acid can create a smoother, more youthful-looking complexion.
Retinoids are vitamin A derivatives known for their ability to stimulate collagen production and improve skin cell turnover. By boosting collagen levels, retinoids can help fill in wrinkles and reduce their depth over time.
Serums containing antioxidants like vitamin C and E can protect the skin from free radical damage, which contributes to aging and wrinkle formation. Antioxidants help maintain skin elasticity and prevent further damage.
While these serums can be effective in reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, they are not a permanent solution like Botox. They work best when used consistently over time as part of a comprehensive skincare routine that includes cleansing, exfoliating, and sun protection.
Finding What Works Best
Consultation with a Medical Professional
Finding a serum that offers similar results to Botox requires understanding the key mechanism behind Botox’s effectiveness. Botox, a purified neurotoxin, temporarily paralyzes muscles by blocking nerve signals, resulting in reduced muscle contractions and smoothing wrinkles.
Arrange a Dermal Filler Consultation at It’s Me and You Clinic with Dr. Laura Geige
While no serum can completely replicate this effect, some ingredients aim to achieve comparable results through different mechanisms:
-
Peptides: Certain peptides stimulate collagen production, improving skin elasticity and firmness. Some examples include Argireline, which is often marketed as a “Botox alternative,” and SNAP-8.
-
Retinoids: These vitamin A derivatives promote cell turnover, boosting collagen synthesis and reducing fine lines and wrinkles.
-
Hyaluronic Acid: This humectant attracts and retains moisture, plumping the skin and temporarily minimizing the appearance of wrinkles.
-
Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs): AHAs like glycolic acid and lactic acid exfoliate the skin, revealing smoother texture and improving overall radiance.
It’s crucial to remember that results from serums will vary significantly depending on individual skin type, concerns, and product quality.
Consultation with a medical professional like a dermatologist is highly recommended to:
1.
Identify your specific needs and goals.**
2.
Assess the suitability of certain ingredients for your skin type and any potential contraindications.
3.
Explore other treatments, such as chemical peels or microneedling, that may be more effective in achieving desired results.
Ultimately, a personalized approach guided by medical expertise can help you find the most effective solution for reducing wrinkles and improving your skin’s appearance.
Individualized Needs and Considerations
Finding the right skincare product can feel overwhelming with the plethora of options available, especially when searching for alternatives to popular treatments like Botox.
While no serum can completely replicate Botox’s ability to temporarily paralyze muscles and smooth wrinkles, certain ingredients can mimic some of its effects.
Understanding individual needs and skin concerns is crucial before diving into serums marketed as “Botox alternatives.” What works wonders for one person might be ineffective or even irritating for another.
Here are some key considerations:
**Skin Type:**
Oily skin might benefit from lightweight, oil-free serums containing ingredients like hyaluronic acid and niacinamide, which can plump the skin and improve texture.
Dry or sensitive skin may require richer serums with hydrating agents such as ceramides, peptides, or aloe vera.
**Specific Concerns:**
Fine lines and wrinkles can be targeted with serums containing peptides like Argireline or Matrixyl, which stimulate collagen production and improve skin elasticity.
Hyperpigmentation might respond well to vitamin C serums, known for their brightening properties.
**Ingredient Compatibility:**
Some ingredients can interact negatively with others. It’s important to research potential interactions before combining multiple serums.
**Individual Tolerance:**
Always patch test a new serum on a small area of skin before applying it to your entire face. This helps identify potential allergies or sensitivities.
**Consult a Dermatologist:**
Book Your Dermal Filler Appointment with Dr. Laura Geige Today
For personalized advice and recommendations, consider consulting a dermatologist who can assess your individual needs and recommend the most suitable serums for your skin type and concerns.
Remember that finding what works best is often a process of trial and error. Be patient, consistent with your skincare routine, and adjust as needed based on your skin’s response.
Lace and Scotch Audrey’s JL Made by Penny Lottie London Aesthetics En Bloch Hotels Emily Patricia Fae
- How To Make CBD Gummies Part Of Your Wellness Routine - May 9, 2025
- Nasal Flare Reduction Near Great Bookham, Surrey - May 8, 2025
- Exosome Therapy For Skin Rejuvenation Near Englefield Green, Surrey - May 8, 2025
